Advanced PFAS Management Solutions to Protect Health
Advanced Methods for Reliable PFAS Contamination Elimination
The consistent obstacle of PFAS contamination necessitates the exploration of sophisticated elimination techniques that can properly address these dangerous materials. Innovative innovations, such as sophisticated oxidation procedures and different adsorption techniques, have become encouraging solutions in mitigating PFAS from affected atmospheres. The function of governing structures in forming these modern technologies can not be overlooked, as they dictate the pace and direction of removal initiatives. As we assess these advanced methods, it becomes essential to assess their useful applications and the wider implications for environmental health and policy.
Comprehending PFAS Features
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) have been widely made use of in numerous industrial and consumer items because of their special residential or commercial properties, their persistence in the setting presents significant obstacles to public health and wellness and safety. PFAS are a team of artificial chemicals defined by a carbon-fluorine bond, among the toughest chemical bonds understood, which adds to their outstanding stability and resistance to deterioration. This stability permits PFAS to build up in the environment and living microorganisms, leading to possible unfavorable wellness impacts.
These same residential properties add to their ecological perseverance, as PFAS do not conveniently damage down via all-natural processes. Understanding the chemical homes of PFAS is necessary for creating effective techniques to handle and reduce their environmental impact.
Innovative Remediation Technologies
The perseverance of PFAS in the setting has actually spurred the development of innovative remediation technologies targeted at properly getting rid of these impurities from impacted environments. Among the most promising methods are innovative oxidation procedures (AOPs), which utilize powerful oxidants to damage down PFAS compounds into much less harmful materials. AOPs can be customized to target details PFAS frameworks, improving their efficacy.
An additional emerging technology is making use of adsorption media, such as triggered carbon and ion exchange resins, which can precisely record PFAS from contaminated water. These products have revealed considerable removal efficiencies, although regular replacement and regrowth are required to keep efficiency.
Membrane purification methods, including reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are likewise gaining grip in PFAS remediation. These approaches can successfully separate PFAS from water, offering a viable solution for dealing with infected sources. In addition, thermal treatment techniques, such as incineration, can decompose PFAS into safe byproducts, though they need careful administration to regulate emissions.
Jointly, these innovative remediation modern technologies represent considerable advancements in the continuous battle against PFAS contamination, offering different strategies to bring back damaged environments and secure public health.

Bioremediation Methods
Bioremediation techniques supply an appealing approach to resolving PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the natural abilities of microorganisms to weaken these consistent substances (m270 waste management). This technique entails using bacteria, fungis, and other germs that can metabolize or transform PFAS materials into much less hazardous results
Recent improvements in molecular biology and environmental microbiology have actually boosted our understanding of microbial neighborhoods and their possible functions in PFAS degradation. Scientists are proactively checking out certain strains of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have shown the ability to break down particular PFAS substances.
In situ bioremediation techniques, where microbes are stimulated directly in from this source infected environments, can be especially reliable. This strategy commonly entails the application of nutrients or electron donors to promote microbial development and task. Additionally, ex situ techniques, such as bioreactors, permit regulated problems that can maximize degradation rates.
In spite of the pledge of bioremediation, obstacles remain, including the intricate nature of PFAS compounds and the need for substantial area screening - m270 waste management. Proceeded r & d will be vital to refine these techniques and analyze their performance in varied ecological contexts
Adsorption and Filtration Approaches
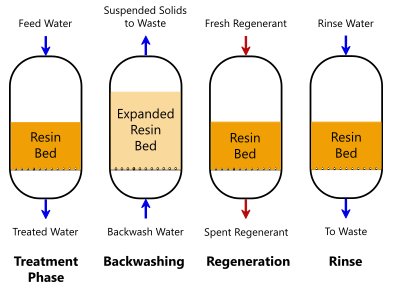
Dealing with PFAS contamination often includes employing adsorption and filtration methods, which are developed to remove these persistent chemicals from water and soil. Amongst the numerous strategies, activated carbon adsorption is widely utilized due to its high surface and porosity, enabling effective capturing of PFAS molecules. Granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems are especially favored for treating large quantities of polluted water, while powdered triggered carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) can be used for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange resins also reveal pledge in PFAS removal, functioning by trading PFAS ions with much less damaging ions in the water. This method has shown performance in concentrating PFAS compounds, promoting their succeeding removal. In addition, membrane layer filtration strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, run by utilizing semi-permeable membranes to different PFAS from water, efficiently decreasing their focus.
While these techniques work, they must be meticulously picked based upon the particular PFAS substances present and the ecological context. Constant advancements in products science and engineering are bring about the advancement of unique adsorbents and filtration systems that boost removal performances and decrease functional costs, consequently boosting total removal efforts.
Regulatory and Plan Factors To Consider
Just how click this site can effective regulative structures boost the administration of PFAS contamination? Comprehensive policies are vital to guarantee a worked with and robust action to the difficulties presented by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) Laws can develop clear standards for monitoring, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, promoting liability amongst sectors and public entities. (m270 waste management)
Furthermore, economic motivations and grants can be integrated right into plans to encourage the adoption of sophisticated removal innovations. Policymakers must additionally prioritize research study and growth, ensuring that emerging methods for PFAS removal are confirmed and carried out properly.
Moreover, public awareness and interaction are important parts of any kind of governing strategy, empowering neighborhoods to support for their wellness and safety and security. Inevitably, a click for info well-structured governing setting will certainly not just boost the monitoring of PFAS contamination yet additionally advertise lasting techniques that secure future generations.
Verdict
In recap, the complexity of PFAS contamination requires the adoption of advanced removal methods. Innovative technologies such as advanced oxidation procedures, adsorption strategies, and membrane filtering have demonstrated significant efficiency in getting rid of these consistent compounds from contaminated water resources. In addition, regulative frameworks should develop to support the execution of these modern technologies, making certain secure and efficient management of PFAS toxins. Proceeded study and growth in this field remain critical to resolving the difficulties posed by PFAS contamination.